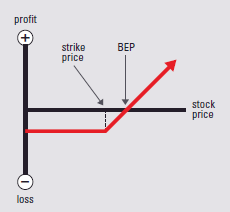
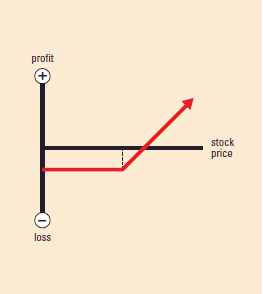
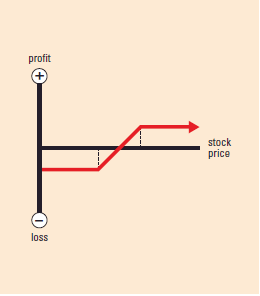
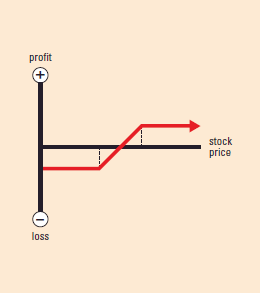
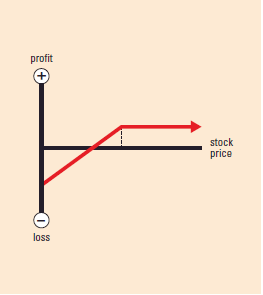
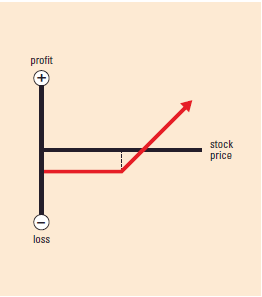
Options Strategies – Each strategy has an accompanying graph showing profit and loss at expiration.• The vertical axis shows then profit/loss scale.
• When the strategy line is below the horizontal axis, it assumes you paid for the position or had a loss. When it is above the horizontal axis, it assumes you received a credit for the position or had a profit.
• The dotted line indicates the strike price.
• The intersection of the strategy line and the horizontal axis is the break-even point (BEP)not including transaction
costs, commissions, or margin (borrowing) costs.
• These graphs are not drawn to any specific scale and are meant only for illustrative and educational purposes.
• The risks/rewards described are generalizations and may be lesser or greater than indicated.
Break-Even Point (BEP): The stock price(s) at which an option strategy results in neither a profit nor loss.
Call: An option contract that gives the holder the right to buy the underlying security at a specified price for a certain, fixed period of time.
In-the-money: A call option is in-the-money if the strike price is less than the market price of the underlying security. A put option is in-the-money if the strike price is greater than the market price of the underlying security.
Long position: A position wherein an investor is a net holder in a particular options series.
Out-of-the-money: A call option is out-of-the-money if the strike price is greater than the market price of the underlying security.A put option is out-of-the-money if the strike price is less than the market price of the underlying security.
Premium: The price a put or call buyer must pay to a put or call seller (writer) for an option contract. Market supply and demand forces determine the premium.
Put: An option contract that gives the holder the right to sell the underlying security at a specified price for a certain, fixed period of time.
Ratio Spread: A multi-leg option trade of either all calls or all puts whereby the number of long options to short options is something other than 1:1. Typically, to manage risk, the number of short options is lower than the number of long options (i.e. 1 short call: 2 long calls).
Short position: A position wherein the investor is a net writer (seller) of a particular options series.
Strike price or exercise price: The stated price per share for which the underlying security may be purchased (in the case of a call)or sold (in the case of a put) by the option holder upon exercise of the option contract.
Synthetic position: A strategy involving two or more instruments that has the same risk/reward profile as a strategy involving only one instrument.
Time decay or erosion: A term used to describe how the time value of an option can “decay” or reduce with the passage of time.
Volatility: A measure of the fluctuation in the market price of the underlying security. Mathematically, volatility is the annualized standard deviation of returns.
bull strategy LONG CALL
Example: Buy call
Market Outlook: Bullish
Risk: Limited
Reward: Unlimited
Increase in Volatility:Helps position
Time Erosion: Hurts position
BEP: Strike price plus premium paid
bull strategy BULL CALL SPREAD
Example: Buy 1 call;
sell 1 call at higher strike
Market Outlook: Bullish
Risk: Limited
Reward: Limited
Increase in Volatility:
Helps or hurts depending
on strikes chosen
Time Erosion: Helps or hurts depending on strikes chosen
BEP: Long call strike plus net premium paid
bull strategy BULL PUT SPREAD
Example: Sell 1 put;
buy 1 put at lower strike with
same expiry
Market Outlook:
Neutral to bullish
Risk: Limited
Reward: Limited
Increase in Volatility:
Typically hurts position slightly
Time Erosion: Helps position
BEP: Short put strike minus credit received
bull strategy COVERED CALL/BUY WRITE
Example: Buy stock; sell calls
on a share-for-share basis
Market Outlook: Neutral to
slightly bullish
Risk: Limited, but substantial
(risk is from a fall in stock price)
Reward: Limited
Increase in Volatility:
Hurts position
Time Erosion: Helps position
BEP: Starting stock price minus
premium received
bull strategy PROTECTIVE/MARRIED PUT
Example: Own 100 shares of
stock; buy 1 put
Market Outlook: Cautiously
bullish
Risk: Limited
Reward: Unlimited
Increase in Volatility:
Helps position
Time Erosion: Hurts position
BEP: Starting stock price
plus premium paid
https://www.pipsafe.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Options-Strategies.pdf
To read More,Please Download the book.
By optionseducation.org
Categories :
Tags : binary options learn books bull strategy BULL PUT SPREAD bull strategy COVERED CALL/BUY WRITE bull strategy LONG CALL BUY WRITE COVERED CALL Download Options Strategies Long position Options Strategies Download optionseducation Put Ratio Spread Strike price plus premium paid trading binary options strategies and tactics pdf free